Diabetes is a disease in which the blood sugar level is higher than the normal range. It is on the top list of diseases known to cause death. Problems in the kidney, lower limb and eye are brought about by Diabetes.
What are the major complications of Diabetes?
The risk for various major health conditions is high for people with Diabetes. Prolonged high blood glucose levels can lead to significant disorders of the heart, eyes, nerves, kidneys, blood vessels and teeth.
Also, people with Diabetes are more likely to contract infections owing to their weak immune systems. Diabetes is one of the foremost causes of kidney failure, cardiovascular illness, blindness and lower limb amputation in practically all high-income countries.
Types of diabetic complications
Complications of Diabetes are categorised based on the time it takes for the disease to commence and last.
Acute complications
Acute or short-term complications are known to occur at any time. They can eventually lead to chronic or long-term complications.
Chronic complications
Chronic or long-term complications arise over time according to the influence of blood vessels on blood glucose levels. High blood glucose levels can harm the body's small and large blood vessels with time.
Acute complications
Life-threatening situations can develop swiftly. Inconsistency between insulin availability and requirement can result in uncontrolled high blood sugar levels and low blood sugar levels, leading to acute complications. Acute complications may necessitate prompt medical intervention in a few cases.
Hypoglycaemia

Hypoglycaemia is defined as a low blood glucose level. The blood glucose level may decrease, especially if a person is on insulin or a sulfonylurea medication. When a person is on these medications and eats in reduced quantity or becomes more active, the blood glucose levels may drop too low.
Certain drug usage and excessive alcohol intake can also lead to Hypoglycaemia. Medication such as aspirin reduces blood sugar levels if taken in large doses. High alcohol intake hinders the release of glucose from the liver.
The signs and symptoms of low blood sugar are:
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat)
- Pale skin
- Anxiety
- Slurred speech
- Headache
- Numbness in toes, fingers and lips
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
Drinking orange juice or consuming glucose tablets will immediately raise the blood glucose level in mild cases of Hypoglycaemia.
Hyperglycaemia
Hyperglycaemia, also referred to as hypers, serves as the cause of major complications, including Diabetic ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic state.
Inadequate insulin causes excess glucose in the blood leading to Hyperglycaemia.
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic Syndrome
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic Syndrome (HHS) is a rare and threatening diabetic complication. HHS develops when a person's blood glucose levels are abnormally high, causing acute dehydration and confusion along with increased thirst.
A person is more prone to HHS when they are sick and aged. This commences when the blood sugar levels begin to rise. When this occurs, the body eliminates excess glucose through frequent urination. As a result, the body gets dehydrated and induces thirst.
When the cells aren't rehydrated, the blood glucose levels rise, and it ultimately peaks, leading to coma.
Keeping a close eye on the sugar levels is necessary to avoid a Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic state.
Symptoms of HHS include,
- Frequent urination
- High blood sugar level
- Loss of vision
- Fever
- Excessive thirst and dry mouth
- Weakness or paralysis
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) occurs when high levels of ketones are produced by the body leading to severe complications. DKA arises when there is not enough insulin for glucose utilisation.
Due to this, the body relies on fat for energy, resulting in the formation of ketones. Acidosis occurs with a rise in the production of acetoacetic acid and 3-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and a decrease in their utilisation. Ketones leak into the urine, making urine test an important diagnostic examination for DKA.
Common symptoms of Diabetic ketoacidosis include,
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Headache
- Dehydration
- High ketone levels in the blood
- Elevated blood sugar levels (>250 mg/dL)
- Abdominal pain
- Fruity-smelling breath
- Confusion
Diabetic ketoacidosis happens suddenly and can develop in a short span of 24 hours. Vomiting can hasten its occurrence. Therefore, it is critical to contact a doctor on noticing symptoms to receive early treatment.
Chronic complications
Chronic problems usually develop over a period of years or decades. Since damage often occurs before symptoms become evident, frequent screening is recommended to detect and address problems before they manifest or worsen.
Microvascular complications
The small blood vessels in the body can be injured over time when a person has consistently high blood glucose levels. Problems in the eyes, nerves and kidneys emerge when the damaged arteries fail to efficiently deliver blood to certain organs.
Eye problems (Diabetic Retinopathy)
Long-term high blood glucose levels can develop cataracts or Diabetic Retinopathy in the eyes, which can result in eyesight loss.
Maintaining blood sugar levels and consulting an ophthalmologist to perform yearly eye examinations can help avoid Diabetes-related related eye diseases.
Nerve damage (Diabetic Neuropathy)
Diabetic Neuropathy occurs when the nerves are injured due to Diabetes. Nerves are supplied with blood through small blood vessels. Their damage will eventually affect the nerves.
Peripheral, autonomic, focal or proximal are classifications of Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy is the most prevalent type of nerve injury. It mostly affects the nerves that go through the hands and feet.
People can lose the sensation in their feet when they have uncontrolled Diabetes for a prolonged time. This can also be accompanied by numbness, tingling sensation or discomfort.
Sore on foot is a severe problem for people with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in the feet. The sores might develop into infections when left untreated. The infection has the potential to spread, and the foot may need to be amputated to prevent the infection from spreading further.
Podiatrists treat foot injuries. Regular checkup with a podiatrist and diabetologist is necessary to prevent infections.
Kidney problems (Diabetic Nephropathy)
Degeneration of kidney function is termed Diabetic Nephropathy. Untreated kidney diseases lead to reduced kidney function, dialysis or kidney transplantation. Unmanaged Diabetes can result in renal failure, where the kidneys are unable to effectively filter the blood.
One of the early symptoms of kidney issues is Microalbuminuria. Testing this can help prevent Diabetic Nephropathy. Once Microalbuminuria is diagnosed, medications can avoid the disease progression.
Macrovascular complications
Macrovascular complications are brought about by Hyperglycaemia, insulin resistance and increased fatty acids. Diseases of the cerebrovasculature, peripheral arteries and coronary arteries result in macrovascular complications of Diabetes.
Atherosclerotic plaque in the blood vessels delivering blood to the brain, heart and limbs is linked to early macrovascular disease.
In the later stages, the vessels are completely obstructed, increasing the risk of stroke, myocardial infarction and gangrene. In diabetic individuals, Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality.
Stroke
Diabetes has long been perceived as a risk factor for stroke. It can produce pathologic changes in various sites in the arteries, and if cerebral vessels are directly damaged, it can lead to stroke.
Furthermore, patients with uncontrolled glucose levels had a greater death rate. Excess blood glucose might lead to an increase in fatty deposits or blood vessel clots over time. These clots can constrict or clog blood vessels in the brain and neck, cutting off blood flow and preventing oxygen from reaching the brain, resulting in a stroke.
Foot problems
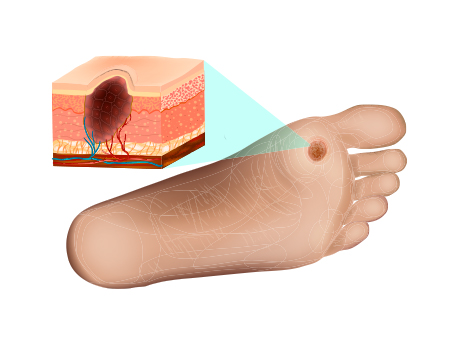
Foot problems are frequently experienced by patients with Diabetes. When high blood sugar injures the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, it leads to foot problems.
Diabetic Neuropathy is nerve degeneration that can cause numbness, tingling sensation, pain or lack of feeling in your feet.
When a person with Diabetes has a wound or a cut, the lack of blood flow hinders the healing process. Sometimes, amputation is needed to treat such conditions. Amputation is a procedure that involves cutting off a damaged leg, foot or toe. It has the potential to stop a serious infection from spreading and perhaps save lives.
Gum disease
Periodontal diseases are the infections of the gums and bones that hold the teeth in place. Gum diseases arise when Diabetes is not effectively managed. The body's reaction to gum diseases might also cause blood sugar problems.
Changes in the blood vessels occur as a result of Diabetes. Thickened blood arteries impede nutrient flow and waste disposal from the tissues. The diminished blood supply can result in weakened gums and bones, making them more susceptible to infection.
Cancer
Type 2 Diabetes doubles the risk of liver and pancreatic cancer. They are also at a larger risk of other cancers like colon, breast and bladder cancer than the general population. The mortality rate is higher when cancer patients have Diabetes as a co-morbidity.
Surprisingly, Diabetes male patients have a lower risk for prostate cancer.
Sexual problems in women
Diabetes can cause sexual issues in women. Uncontrolled high blood sugar for a long time can harm nerves and blood vessels, especially those required for sexual function.
It also has the potential to reduce blood flow to the genitals, which is necessary for increased feeling and lubrication.
Some frequent Diabetes complications that women face:
- Low arousal and desire.
- Physical sensibility is limited.
- Vaginal dryness
Sexual problems in men
Low libido or sexual drive is a severe condition that affects diabetics more than non-diabetics. Diabetes leads to low testosterone levels, which influence a man's desire for sex.
The inability to have an erection is one of the most common sexual difficulties that men with Diabetes confront. The reduced blood supply to the penis due to vascular system injury makes it harder to get an erection.
Neurovascular damage, impaired blood flow and reduced sensation can make it difficult for men to reach orgasm.
Peyronie's disease is more common in men with Diabetes. It is a disorder in which scar tissue inside the penis causes a bent and painful erection.
Lifestyle modifications and regular doctor checkups serve to prevent such complications.
Causes of complications associated with Diabetes
Prolonged fluctuations in blood sugar levels in a diabetic person can lead to short-term and long-term problems.
Since the onset of type 2 Diabetes is slow, high blood glucose levels can be noticed for a long period. This might lead to complications over time.
Smoking, high blood pressure and increased fat content in the blood can harm the blood vessels, causing a greater risk for Diabetics.
How to prevent or delay complications?
Controlling blood sugar, blood pressure, and blood fats will greatly lower the risk of diabetic complications.
Managing Diabetes
Patients diagnosed with Diabetes have to be aware of the disease and its complications. Blood sugar levels and HbA1c have to be maintained in the target range to reduce risk. Other factors like blood pressure and cholesterol levels must also be maintained to prevent consequences.
Healthcare professional, including a doctor, has to be consulted for treatment. This can bring back the levels within the desired range and avoid complications.
Stop smoking
Smoking causes insulin resistance, leading to high blood glucose levels. Quitting smoking can help to safeguard against diseases. It is said that diabetic people who quit smoking have better blood sugar control.
Studies prove that insulin works effectively by lowering blood sugar levels post quitting smoking in diabetic individuals. Nicotine replacement therapies and products can be used as tools to stop smoking.
Eat healthily
Diabetes can be managed with a healthy diet pattern. Seeking the advice of a professional would be of great use.
Foods low in calories, fats, sugar and salt are considered ideal for a diabetic. Lean meat is preferable in comparison to fatty meat. Choosing foods high in fibre and including vegetables in the diet helps to maintain blood glucose levels.
Be active
Physical activity is required for any individual and is crucial for a person with Diabetes.
A person can be more active by setting goals and engaging in physical activity for at least five days a week. Beginners can start with 10 minutes walk per day.
Muscle strength can be targeted by working out twice a week. This can be done with the help of yoga, stretch bands and strength training workouts. A healthy weight can be achieved with a proper diet and exercise.
Conclusion
One of the significant health concerns prevailing around the world is Diabetes. Diabetes raises the risk of Retinopathy, renal disease, myocardial infarction, heart failure, liver disease and stroke.
The complications can be categorised as acute and chronic. Managing blood sugar levels is pivotal to preventing or reducing the effects of complications. Being active, keeping the blood glucose levels in check, and engaging in healthy eating habits are important to combat Diabetes-related complications.
FAQ's
What is the most common complication of Diabetes?
What causes chronic complications of Diabetes Mellitus?
What is the treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy patients?
What can I eat if I have Diabetes?
What should my blood sugar level be?
Is Diabetes difficult to control?
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels are treated with medications and rarely with insulin. Treatments are also available for Diabetes-related complications, making Diabetes manageable to control.
What resources are available to help me control Diabetes?
Medications and insulin are commonly available resources for controlling Diabetes, along with healthy food.
Should I follow a low-carb diet?
In a few cases, a low-carb diet is more likely to cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. So, it is always recommended to consult a dietitian before following a specific diet. A dietitian can provide a personalised diet plan to treat Diabetes.